 The division cams and trip levers.
The division cams and trip levers.
The Madas performs automatic division by the subtract-and-shift method, under the control of a set of auxilliary cams and intermittent gearing located towards the rear of the right-hand side plate.
 The division cams and trip levers.
The division cams and trip levers.
This photo shows only the essentials of the division mechanism.
Division proceeds by subtraction until the accumulator register goes negative, at which time a carry out of the tenth decade trips the four-armed lever to the upper right of the main drive gear. The lower arm on this lever tries to push the division camshaft anti-clockwise to engage with the mainshaft gear.
The intermittent gearing picks up at 325 degrees, and quickly rotates the division camshaft one-third of a turn. The innermost cam pushes rearward on the horizontal link to the differential positioning arm, forcing the arm against the spring and into the "add" position. The forked link reverses the direction of the counter register, and the machine performs an addition cycle.
 Initiating the carriage shift.
Initiating the carriage shift.
At the end of the addition, the intermittent gearing rotates the camshaft another third of a turn and restores the differentials to "subtract".
The third cam operates via an intermediate lever (lower centre) to trip the carriage shift request shaft (lower right). The machine then completes a left-shift cycle. The accumulator and counter registers are automatically inhibited during the shift.
On completion of the shift, the camshaft rotates back to its home position, and the machine continues with subtract cycles in the new carriage position.
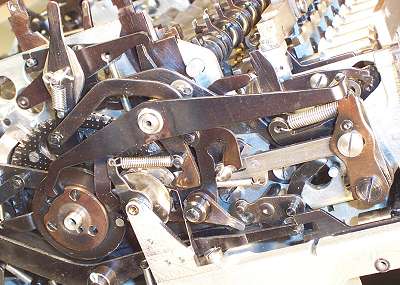 The mechanism fully assembled.
The mechanism fully assembled.
This view shows the division mechanism fully assembled. There are several interlocks, and a mechanism to terminate the division when the carriage reaches the extreme left.
There is an ingenious mechanism attached to the "Add +/-" lever (upper left) which allows the user to select normal or complement for the counter register during division, and yet reverses either selection automatically during the addition cycles.
The outer lever on the large central pivot is not strictly part of the division mechanism, but serves to ensure that the differential positioning arm is securely locked in either plus, minus, or neutral between about 50 and 320 degrees on every mainshaft cycle.